UX research is incredibly important during the development of a product or service.
Whether you’re building a new ecommerce website, AWS data warehouse architecture, or dating app, UX research is a great way to improve customer satisfaction by providing the best possible user experience.
If you’re looking to improve your product development team, it’s important to hire fullstack developers who have expertise in both front-end and back-end development.
What is UX Research?
User experience (UX) research is the process of learning what is required by the end users of a product, service, or website, and then using those insights to improve the development of their product, remove pain points, and make it more user friendly.
There are two key methods of UX research; qualitative and quantitative. Both are popular methods of measuring the success of design decisions during development.
What is Qualitative UX Research?
Qualitative UX research involves gathering non-numerical data about the user experience. This could take the form of comments, opinions, or behaviors, and can be gathered using interviews, focus groups, or surveys.
The purpose of qualitative UX research is to generate insights into how users feel about products and services, and their experiences using them.
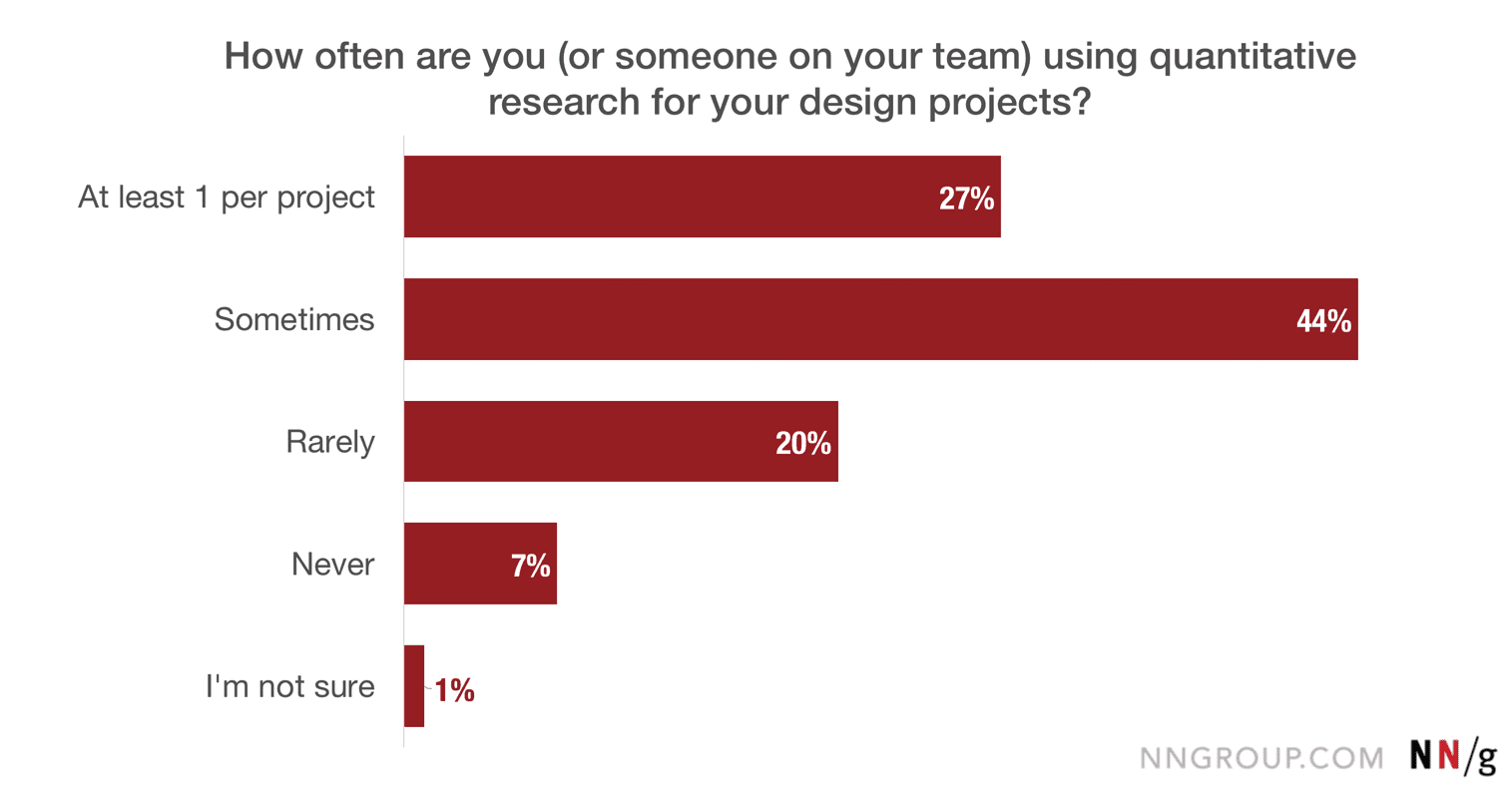
What is Quantitative UX Research?
Quantitative UX research is concerned with gathering numerical data which can yield quantifiable results about the user experience.
It can be gathered in a variety of ways, such as collecting customer data from an ecommerce website, or through user testing sessions.
The data will be used to identify trends and patterns, and measure various metrics, allowing researchers to answer questions such as ‘how many?’ and ‘how often?’
Data collection is a crucial aspect of both qualitative and quantitative UX research, allowing researchers to gather information about user behavior, preferences, and pain points.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Data in UX Research
There are several key differences between qualitative and quantitative data in UX research, giving each approach different uses in different scenarios.
Qualitative | Quantitative | |
Data Collection Methodology | Surveys, focus groups, interviews, heuristic analysis, observations. | Analytics: page visits, bounce rates, conversion rates.User testing sessions: mouse clicks, task completion times, success rates. |
Number of Respondents | Smaller sample sizes are feasible, as there is less of a focus on statistical relevance. | Larger sample sizes yield more data points, which provide more informed conclusions. |
Data Visualization | Word clouds, heat maps, timelines, infographics. | Pie charts, bar graphs, histograms, scatter plots. |
Benefits |
|
|
Qualitative vs. Quantitative UX Research: When Should You Use Which?
Quantitative research will provide you with measurable data points which can be statistically analyzed, while qualitative research will give you more abstract data to work with, such as opinions and motivations. Both approaches have their advantages, so the trick is to know under which circumstances you should use each method.
Qualitative UX research is well placed to discover pain points in a product, giving developers the chance to rectify them to provide a better user experience. For example, users may be experiencing problems with particular integrated apps, which developers could then investigate, and try to make the integrations more intuitive.
For this reason, it’s a good idea to carry out qualitative UX research during the development process, giving users a chance to identify potential problems in early builds of the product
Quantitative UX research, on the other hand, is often used to evaluate metrics on an existing product. In this way, products can be compared against their competitors, and have their usability tested over time.
Because quantitative research often involves using larger sample sizes, it can be more difficult to justify early on in the development process. Qualitative research, however, is more easily justified, as its costs are typically lower when it comes to obtaining testers.
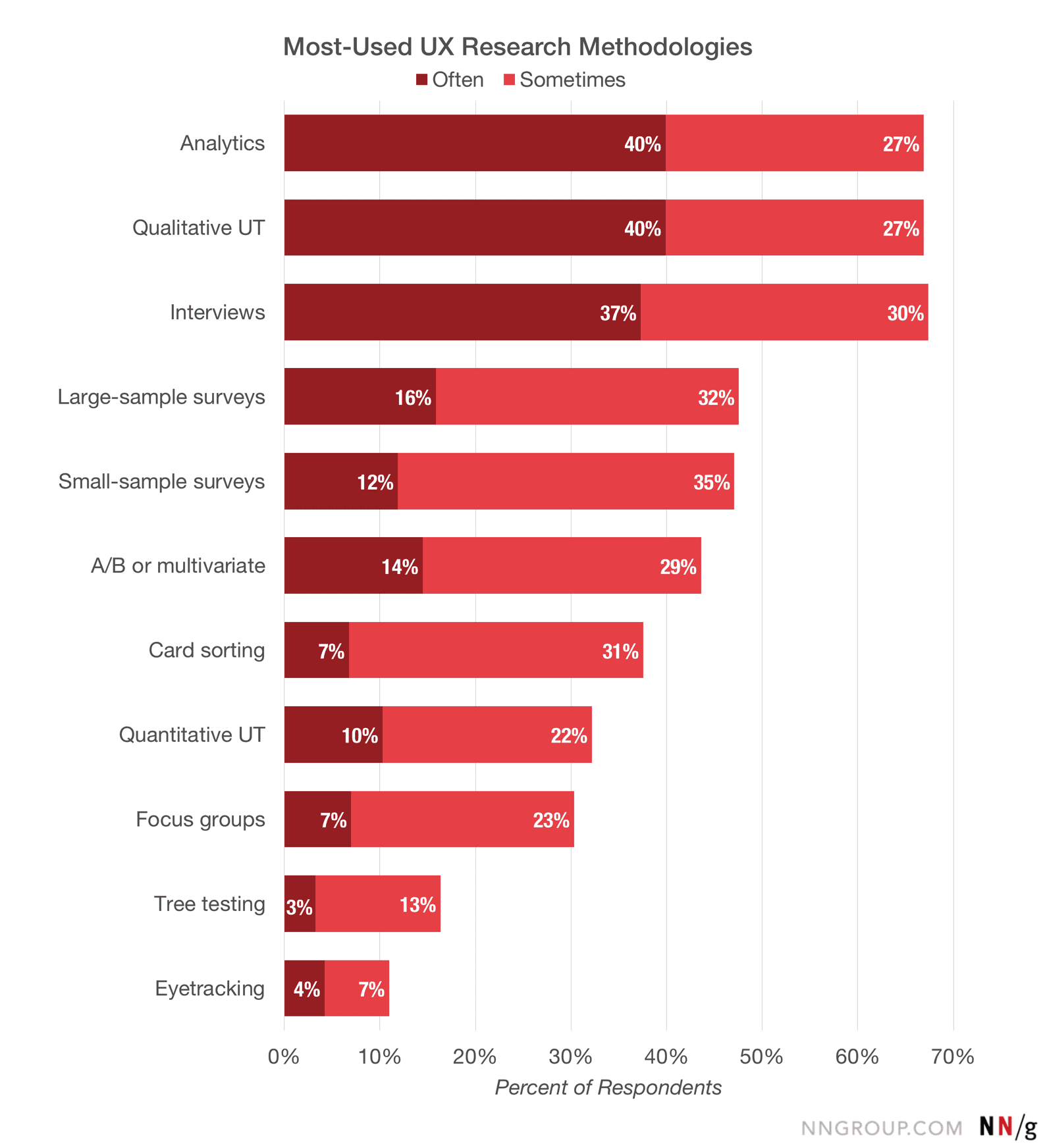
Data Collection Methods
There are various user research methods through which qualitative and quantitative data can be collected.
Qualitative Data
Interviews
Interviews with users who have experience of using the product are an excellent way to gather insights about its usability, pain points, and the overall user experience. These can be carried out one-to-one, or in the form of focus groups.
It’s a good idea to collect insights from a range of users with different backgrounds, such as those who have the best data engineering certifications, mixed with those who are complete computing novices.
Surveys
Depending on the nature of the questions, surveys can be used as either a qualitative or quantitative data collection method.
Open-ended surveys which ask about the users’ thoughts and feelings are a form of qualitative research, as they give the user the ability to go into detail about their experience, and provide contextual information.
In some ways, they form a written version of an interview or focus group, with the added benefit of being able to be distributed to a large number of people, without having to host them.
Diary Studies
Diary studies ask testers to use a product over a longer period of time, recording their thoughts and feelings about their experience, and how it changes during that period.
This provides developers with a wealth of in-depth data, and allows them to see how any changes they’ve implemented during that time have impacted their users, either positively or negatively.
Quantitative Data
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves examining user analytics in order to identify potential pain points for customers and users. For example, high cart abandonment rates on an ecommerce website might indicate that users had problems checking out, and high bounce rates might mean that landing pages need to be better formatted.
Funnel Analysis
Funnel analysis documents how many users complete a number of predetermined actions, and the drop off rate at each point in the funnel. This allows developers to pinpoint which parts of a product or service are causing the most trouble for their users, and act accordingly.
Mouse Heat Maps
Mouse tracking can be used to determine how users have interacted with a website. With enough data, this information can be used to generate heat maps, which will show which aspects of a website are most interacted with, and which are ignored. This can help developers understand where is best to present information, how to arrange interactive elements, and the typical scroll depth of website users.

Use Qualitative and Quantitative UX Research Together for the Best Results
Qualitative and quantitative UX research methods can provide developers with different types of information about how users are interacting with their product or service. However, it’s only by combining the two types of research together that a complete picture can be formed.
Qualitative research allows developers to form hypotheses, and quantitative research provides the raw data to prove or disprove those hypotheses. Using both types of research together allows developers to not only answer questions of ‘how many?’ or ‘how often?’, but also ‘why?
Combine the best of both worlds, and use qualitative and quantitative research to help you build a product that is easy to use, free of pain points, and will leave your customers extremely satisfied.





